LED Technology: Analog Origins & Digital Control
Light Emitting Diodes, or LEDs, are adaptable devices applied in every possible field, from simple indicators to sophisticated electronic display systems. Now, if understanding whether an LED is an analog or digital device is required, this calls for a closer look at the operation and how they were used in different contexts.
Basics of LED
Basically, an LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. During the process of electroluminescence, electrons recombine with holes within the material, releasing this energy in the form of photons. Therefore, the light emission is proportional to the current that passes through the diode; hence, the basic principle of operation of an LED is based on analog operation.
Analog Characteristics
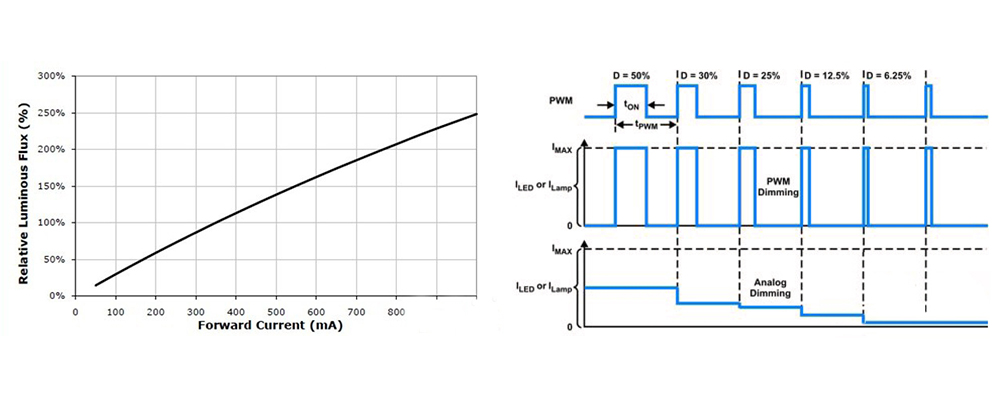
In their simplest nature, LEDs are an analog device. The brightness is proportional to the current passed through the LED. You achieve different degrees of brilliance by altering the flow or amount of current. This is analog behavior hacked for applications like dimming control and variable lighting systems. However, changing the current—for example, through a potentiometer—will also smoothly change the light output, therefore demonstrating the LED's analog nature.
Digital Control
Although an LED is basically an analogue device, they are often controlled by digital means, more so in any modern electronic device. Digital Control: As its name implies, the LED is turned on and off rapidly using a technique called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). PWM switches the LED on and off at a high frequency and, by varying the duty cycle that is, the proportion of time the LED is on versus off, the perceived brightness can be controlled. This method is effective and has wide applications in digital circuits, microcontrollers, and LED drivers.
Applications
-Indicators and Display: In basic indicator uses, LEDs are normally operated digitally. They are either at a fully on or fully off state, indicating the binary states—for instance, power status indicators.
-Lighting Systems: In complex lighting systems, the LEDs are switched by an analog or digital control method. To effectively control with energy saving, PWM—a digital methodology—is often used.
-Communication and Signaling: LEDs are digitally driven in fiber optic communication and data transfer to indicate binary data; hence, this further shows their application in the digital field.
Although the fundamental functioning of an LED is analog—based on the principle of continuous variation of current for brightness modulation—the control mechanisms in use with modern applications are largely digital. It is therefore this blend of analog operation with digital control that makes an LED versatile and appropriate for use in a myriad of applications, extending from simple indicators to sophisticated display and lighting systems. This duality must therefore be kept in mind while using LEDs effectively in both analog and digital electronic designs.



