Ensure Consistency and Color Accuracy with Point-by-Point Calibration for LED Displays
Why do LED display screens need to be calibrated point by point?
No two leds in the world have exactly the same brightness! The inherent discreteness defect of the LED itself, the discreteness of the current in the driver chip and the discreteness of the optical axis cause the brightness error of the LED lamp. Packaging process: The size of the slices, the Angle of die bonding, the position of the soldering wires, the purity of the colloid and other processes, the wavelength and brightness scale of the light separation and color separation, along with the Angle of the manufacturer's lamp insertion, the Angle of the mask, the flatness of the module, the flatness of the box assembly, the different heat uniformity of the screen in later use, the light attenuation of different leds, and many other factors, all affect the normal color reproduction of the LED screen. Commonly known as "flower screen".
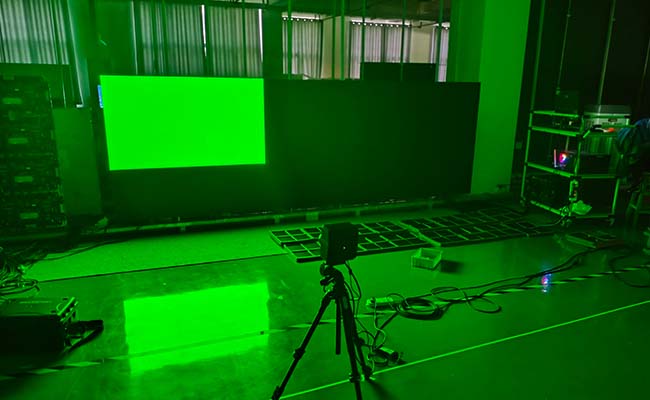

What is point-by-point correction?
Point-by-point calibration is precisely a technology used to enhance the color uniformity and color fidelity of LED displays. That is, by collecting the brightness (and chromaticity) data of each pixel (or each primary color sub-pixel) area on the LED display, it provides the correction coefficient of each primary color sub-pixel or the correction coefficient matrix of each pixel, and feeds it back to the control system of the display. The control system applies correction coefficients to achieve differential driving for each pixel (or each primary color sub-pixel), making the picture of the LED display screen pure and fine, and the colors truly restored.

What preparations should be made before calibrating an LED display screen?
1. Tool preparation: Professional equipment such as spectrometers (such as Konica Minolta CL-500A) and colorimeters for precise measurement of color parameters. Basic tools: laptop (with LED screen debugging software installed), network cable/data cable, screwdriver (for disassembling the module).
2. Clean the LED display screen to remove dust and stains from the lamp surface and mask to avoid their impact on brightness. If you need to replace the mask, please ensure that the color of the mask is the same as before. Otherwise, the display will be affected, especially during the day. Even after calibration, there will be little improvement.
3. Replace malfunctioning modules: those with some lights not lighting up, those with many dead lights, those with abnormal scanning, those with overall lights being too dim (possibly due to incorrect resistance), those with ribbon cables or sockets affecting display, etc. Make sure that the final display, scan and picture are normal, without any phenomena such as being too dark, constantly on or continuously on.
4. Receiving card upgrade: If the currently used receiving card does not support calibration or has insufficient load points, an upgrade is required.
5. Calibration collection should be carried out in an environment free from wind, rain and fog interference, or relevant measures should be taken to ensure that the collection equipment collects accurate data as much as possible in an interference-free environment, ultimately achieving the best calibration effect. Turn off unnecessary light sources around indoors and keep the ambient light uniform and stable (it is recommended to use D65 standard light sources). Clean the dust on the screen surface to avoid stains affecting the measurement accuracy.
6. Confirm that the debugging software provided by the LED screen manufacturer has been installed, and be familiar with the core functional modules such as "color calibration", "brightness adjustment", and "point-by-point correction".
Note: Brightness correction only improves the uniformity of full-screen display or resolves practical issues caused by inconsistent brightness by reducing the brightness of some light points. It cannot increase the brightness of the lights, change the Angle of light emission, or correct other display problems caused by hardware function issues (power supply, resistance, ribbon cable).
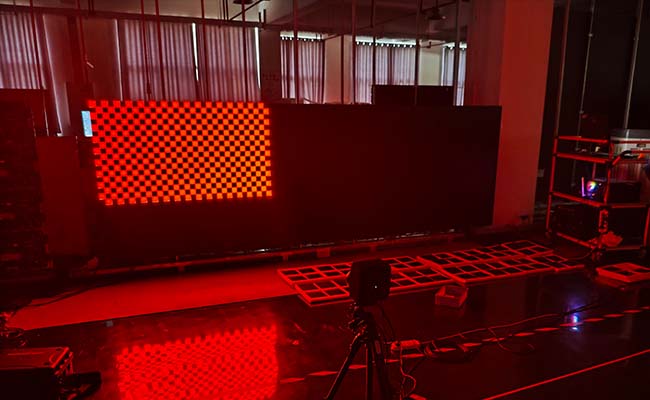

Point-by-point correction operation steps
1. Adjustment of basic parameters
- Brightness and Contrast: Set the screen brightness to 1.5 to 2 times the ambient light (for example, if the indoor ambient light is 300lux, adjust the screen brightness to 500 to 600cd/㎡), and control the contrast at 80% to 90% to avoid color loss caused by excessive brightness or darkness.
- Color temperature selection: 6500K (cold white) is commonly used in the broadcasting and television field. For conference rooms and exhibition halls, 5500K-6000K (natural white) is recommended to create a comfortable visual experience.
- Gamma curve: The default setting is 2.2, but it can be adjusted according to the actual brightness of the picture (if the picture is too dark, appropriately increase the gamma value to 2.4).
2. Point-by-point correction to eliminate "pigmentation spots"
- Data collection: Activate the "point-by-point correction" function of the debugging software, and scan the red, green, and blue primary color brightness of each module through a spectrometer to generate raw data.
- Focus on marking areas where the brightness deviation exceeds 5% (such as corner modules and splicing gaps).
- Parameter correction: Based on the measurement data, fine-tune the RGB brightness values of the outliers in the software (usually, each adjustment does not exceed 3%).
- Calibrate and compare the picture effects multiple times until the entire screen has uniform brightness and color.
3. Gamma and Color Temperature Fine-tuning Gamma curve optimization
- Import industry standard Gamma curves (such as sRGB), observe whether the details in the dark areas of the picture are clear and whether the bright areas are overexposed. If necessary, manually fine-tune the control points.
- Color temperature calibration: Measure the actual color temperature of the screen through a spectrometer, compare it with the target color temperature, and fine-tune the RGB gain value (if the actual color temperature of 7000K is too high, appropriately reduce the blue channel gain).
Point-by-point correction is particularly important in COB LED displays, which can ensure better consistency of the LED display screen, achieve consistency in brightness and chromaticity of high-quality LED displays, and improve the display quality of the screen.



